Leitat Technology Center
Barcelona, Spain

Energy
label
Natural
lighting
of workspaces
Proximity materials
of total cost
Reusable
materials
of total cost
Recyclable
materials
of total cost
Deconstruction
except foundations
Project details
Location: C/ Pallars, 179-185, Barcelona, Spain
Year: 2014
Surface: NA
Status: Built
Typology: Tertiary
Category: Colaboration R+D, Applied sustainability, Environmental certifications
Energy demand verification and calculation from Energy Plus simulation
Collaboration with LAVOLA to monitor the building
Certifications
GREEN certification “FOUR LEAVES”.
Objetivos de desarrollo sostenible







Purposeful analysis of bioclimatic and environmental aspects
Objective: to conceive the building according to the criteria of circular economy
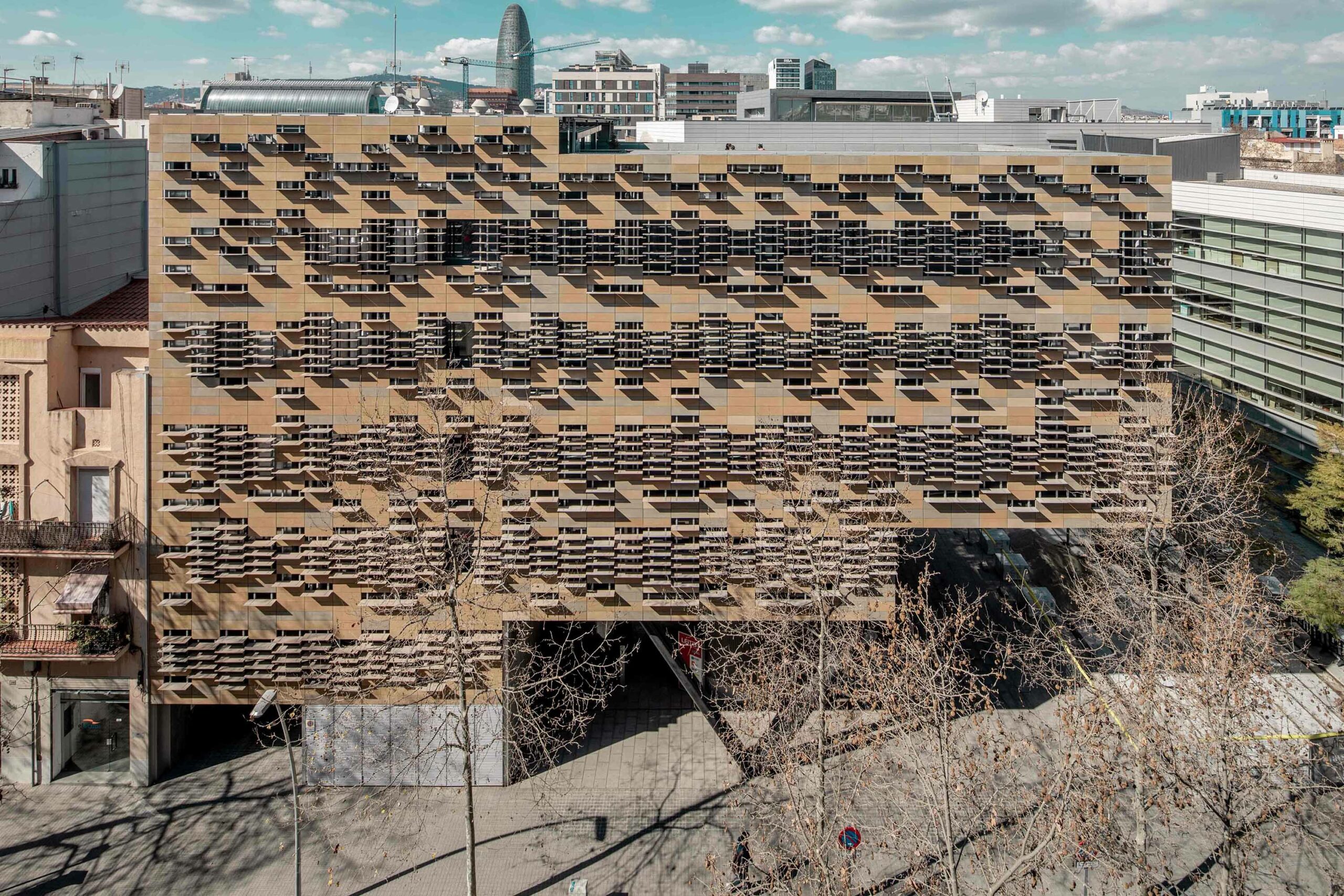
The building is located in the 22 @ Innovative District of Barcelona and is intended for applied research, in the fields of Biotech, Nanotech and new technologies, where the reduction of materials, costs and energy consumption is compatible with a positive impact both at the urban level as functional.
The building has obtained an A energy certification and a Green 4-leaf environmental certification from the Green Building Council.
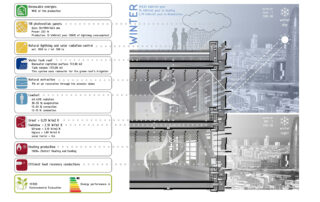
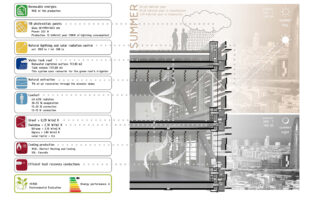
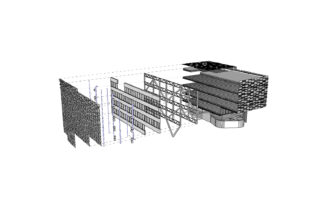
ENVELOPE
The building has been designed to act as an interface or balancer between the indoor and outdoor climate conditions, like a membrane that filters and exchanges with the surrounding conditions.
Outer Layer: A horizontal slat protects and diffracts the bounced light towards the interior. A vertical mineral slat integrates with the adjoining urban space, the material is made up of photocatalytic microparticles.
Middle Layer: Ventilated chamber. Integrates all vertical lines of facilities. All facilities are registrable.
Interior Layer: A sandwich panel composed of a waterproof sheet, rock wool insulation and recycled aluminium carpentry strictly performs its function with the most suitable material, without the need for an exterior appearance.
ROOF
Ecological cistern. Community living space. Rainwater store. It restores the impact of its construction with vegetation.
Rainwater catchment area: 172.80m2.
Tank capacity: 17,318m3.
Landscaped area: 172.80m2.
FACILITIES
District Clima 22@: 90% of the air conditioning consumption is covered by the heat and cold network (99.28kWh / m2 year).
Heat recovery equipment (70-73%). Air renewal through cellular slabs.
Photovoltaic: 118 collectors. Production: 24,719.4 kWh / year. All lighting is covered.
Lighting: 83.22% of workplaces have natural lighting.
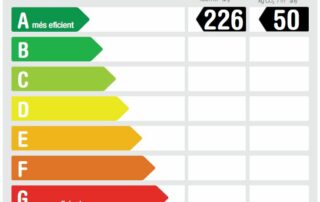
BUILDING CONSUMPTION:
226.09 kWh / m2 year of primary energy.
107.02 kWh / m2 of final energy (99.29 kWh / m2 year air conditioning consumption. 7.75 kWh / m2 year lighting consumption). Consumption does not take into account office equipment.
EMISSIONS OF GREENHOUSE GASES
50 kgCO2 / m2 year (45.63 kg CO2 / m2 year for air conditioning and 4.74 kgCO2 / m2 year for lighting)
The building has an energy remote management system.
BUILDING CONSTRUCTION
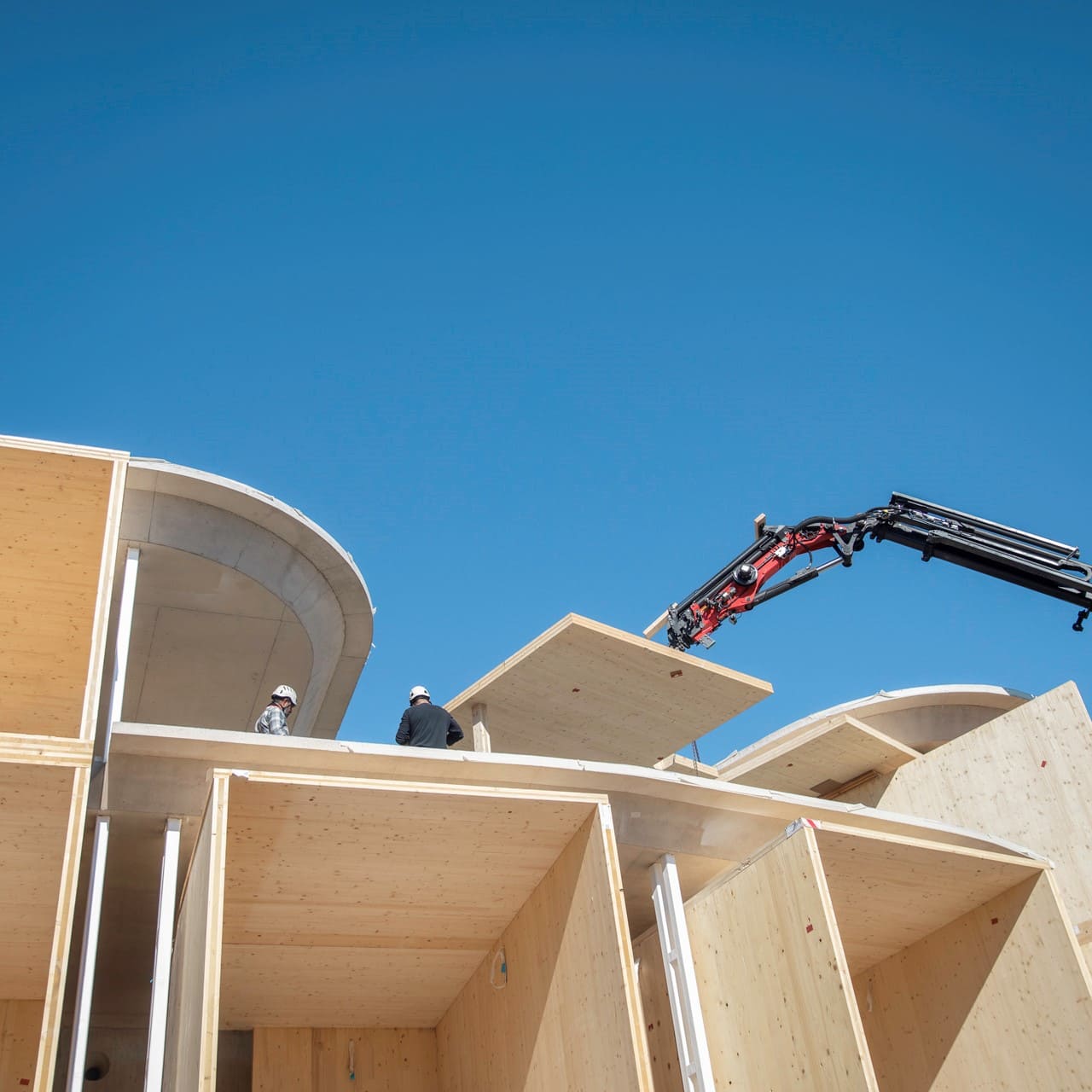
The building is produced in the factory, assembled on-site and consequently can be dismantled and returned to nature, or as a new recycled and reused raw material.
Proximity materials: 60% of the budget
Reusable materials: 42% of the budget
Recyclable materials: 66% of the budget.
Deconstruction: 100% not including foundations.
Contribución a los ODS
Nivel de influencia: ● ● ● Directo – ● ● ○ Medio – ● ○ ○ Indirecto

4. Educación de calidad
● ● ○ 4.5 Eliminar toda discriminiación en la educación
● ● ○ 4.7 Educación para el desarrollo sostenible y la ciudadanía mundial

6. Agua limpia y saneamiento
● ● ● 6.3 Mejorar la calidad del agua. Reducir la contaminación y aguas residuales.

7. Energía asequible y no contaminante
● ● ● 7.2 Aumento de las energías renovables.
● ● ○ 7.3 Duplicar la tasa mundial de mejora de la eficiencia energética.

8. Trabajo decente y crecimiento económico
● ○ ○ 8.2 Elevar la productividad a través de la diversificación, tecnología e innovación.

9. Industria, innovación e infraestructura
● ○ ○ 9.1 Desarrollo de infraestructura sostenible.
● ● ● 9.4 Modernización de la infraestructura, tecnología limpia.
● ○ ○ 9.5 Aumento de la investigación científica, capacidad tecnológica.

11. Energía asequible y no contaminante
● ○ ○ 11.2 Proporcionar el acceso al transporte público
● ● ● 11.3 Aumento de la urbanización inclusiva y sostenible
● ● ● 11.7 Proporcionar el acceso a zonas verdes y espacios públicos seguros.

12. Producción y consumo responsable
● ○ ○ 12.4 Gestión de los desechos y productos químicos.
● ● ○ 12.5 Prevención, reducción, reciclado y reutilización de desechos.
● ○ ○ 12.8 Asegurar la educación para el desarrollo sostenible.