Altener Program of the European Commission
Energy saving studies from the project. Application in two housing projects.

Project details
Years: 1999-2001
Firm role: “Altener Program” of the European Commission 1999-2001 for an extrapolable study on the incorporation of passive and active energy saving systems in urban areas.
Category: Applied Innovation, European Projects
Partners:

Collaborators: Work team in the “Altener Program”: TIRONNE NUNES URBANISMO, LDA with CEETA, EBO CONSULT with CENERGÍA, EMMA, PICH-AGUILERA ARQUITECTOS, S.L with INSTITUT CERDÀ
The interaction between the different teams of architects, engineers, researchers together with the possibility of counting on experts in calculations and simulations made it possible for the Project to be enriched as the analyses developed by the research were incorporated.
Application projects:
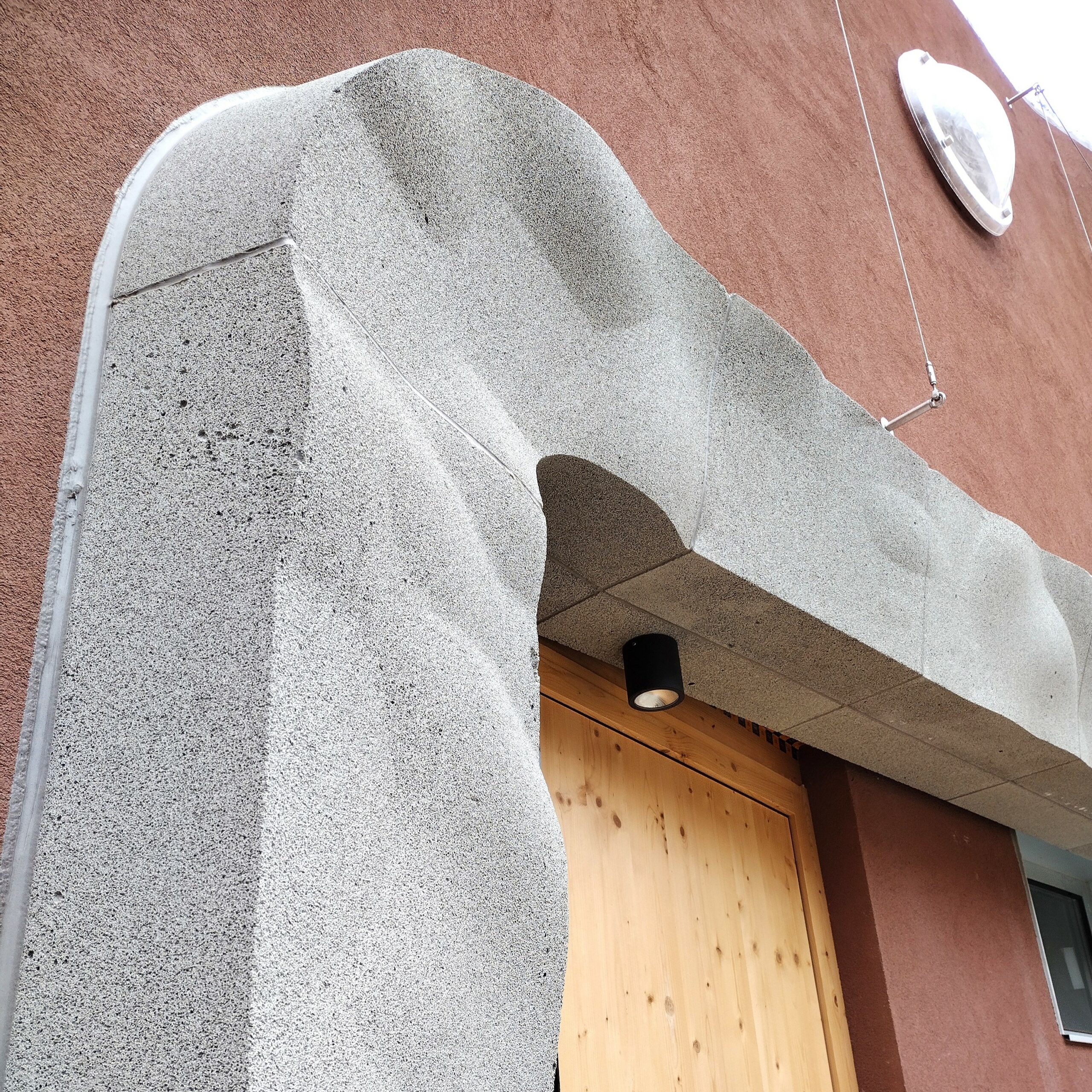
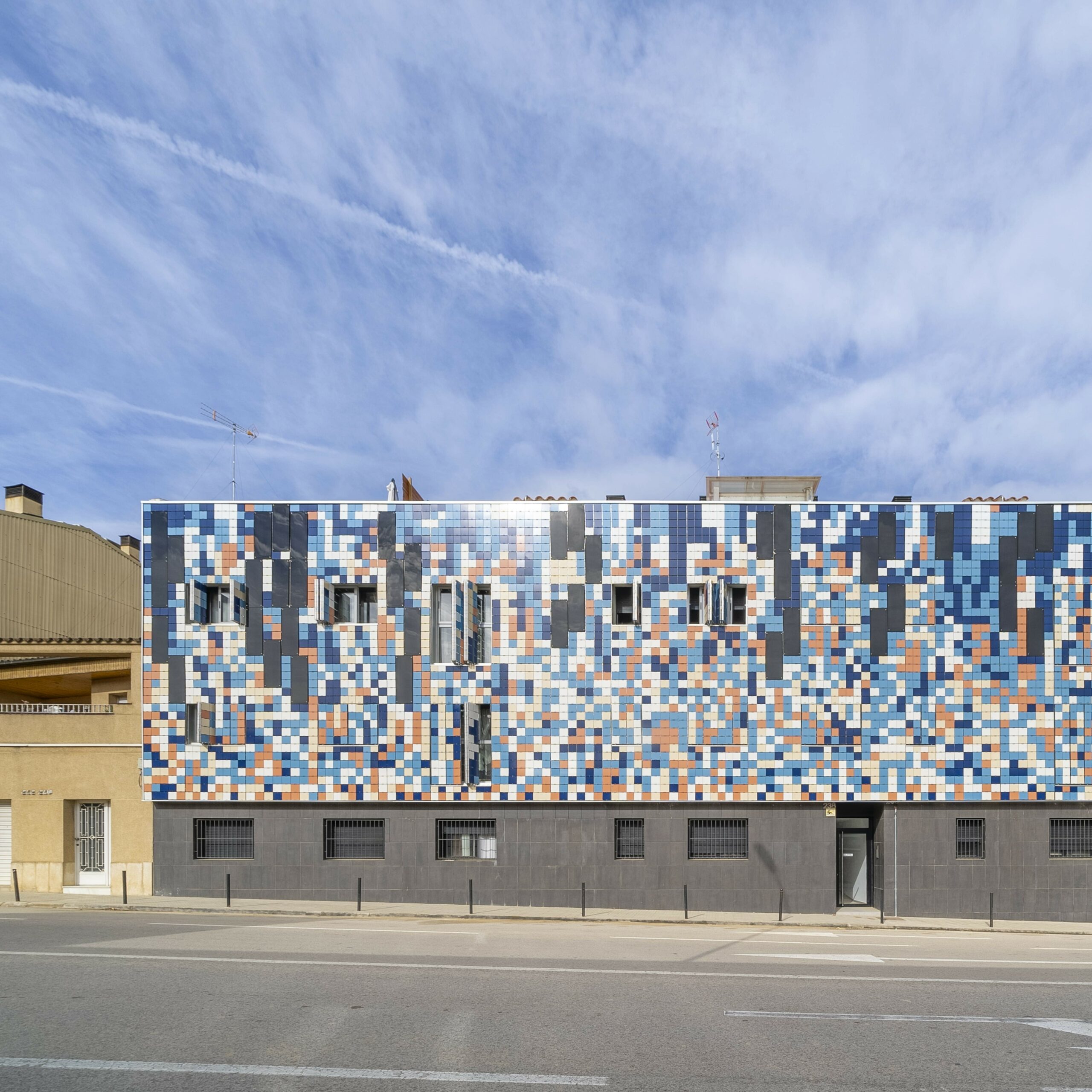
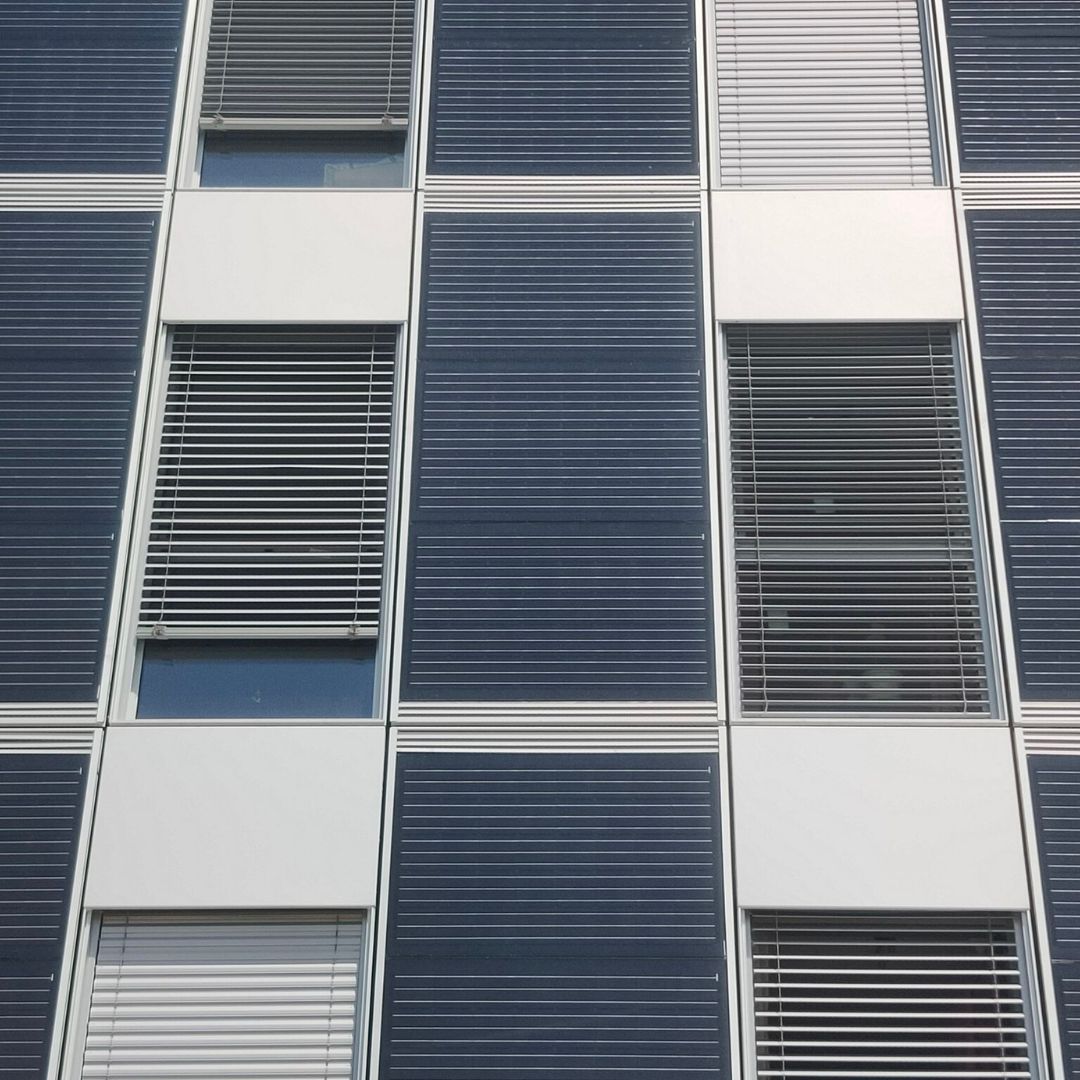
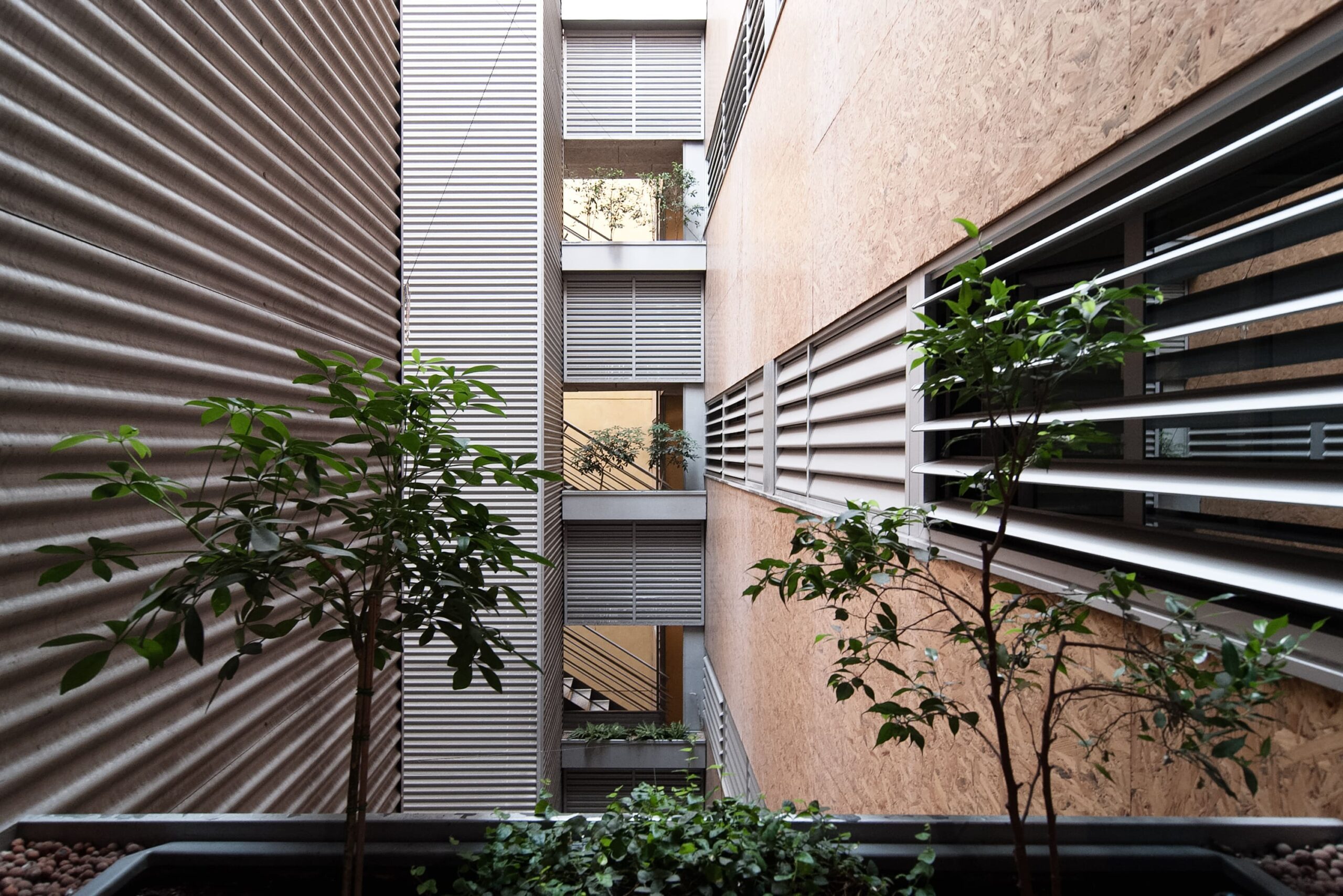
Free housing in the Eixample district of Barcelona “Pau Claris building”. Completed in 2004.
The building mainly considered these aspects:
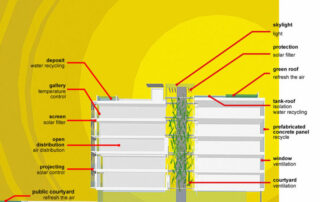
- Analysis of the skin of the building enclosure, that is to say, facade, roof and interior facades.
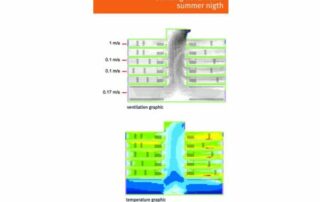
- Natural ventilation systems through a lobby /central courtyard
- Structural and construction systems.
- Consumption management. Calculation of energy savings and thermal simulations.
- Analysis of possible improvements in materials with low environmental impact
- Introduction of construction elements that favour the environment.
- Vegetation is a regulator of humidity and temperature.
- Eco-materials
- Recycled materials
All these aspects were studied from its technical specifications, testing during the simulation development and costs in relation to the costs of a conventional building.
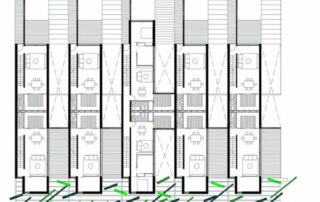
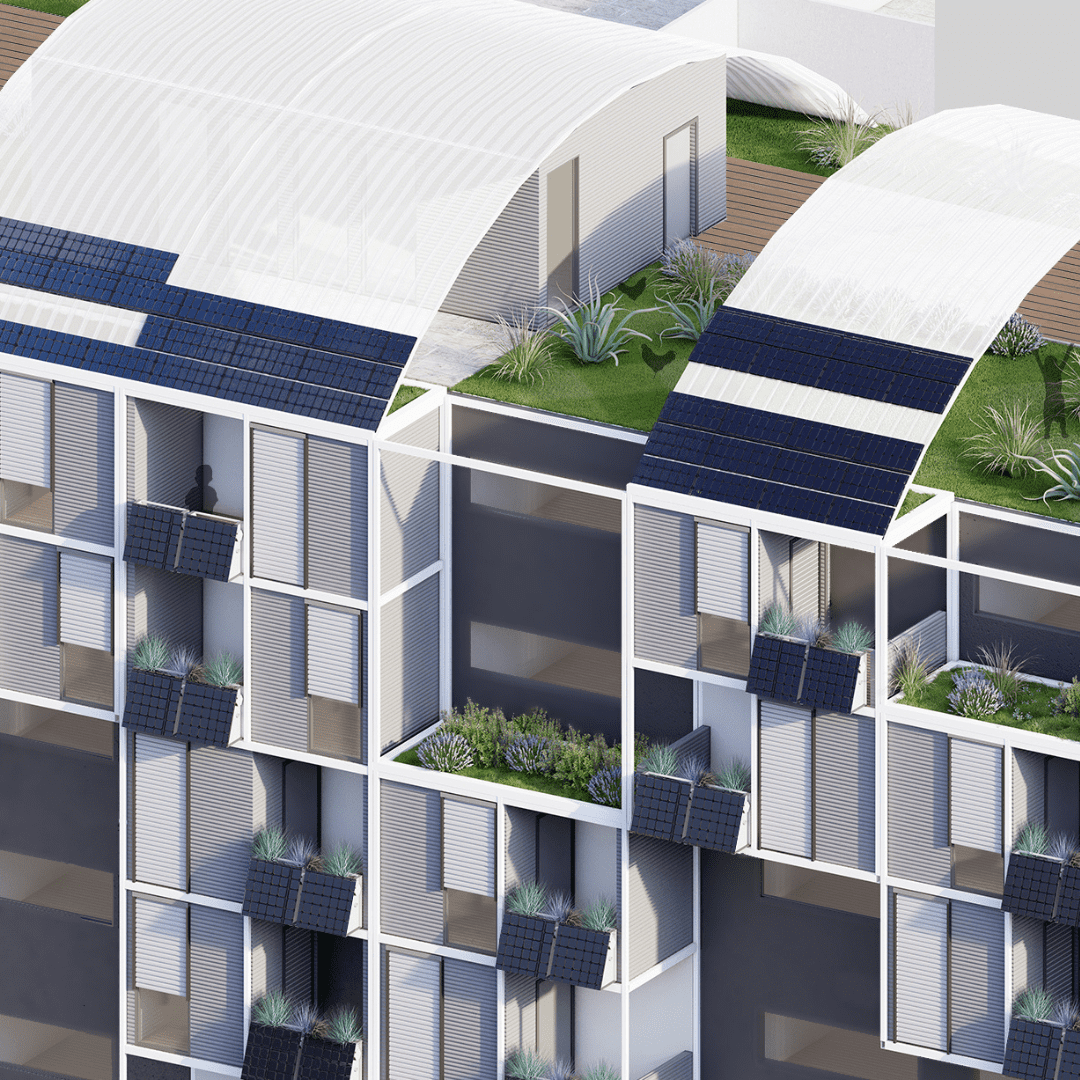
Social Housing in the city of Alguazas, Murcia (First Prize EUROPAN III).
The basic project and the construction project were developed. It was not built.
The residences considered these aspects:
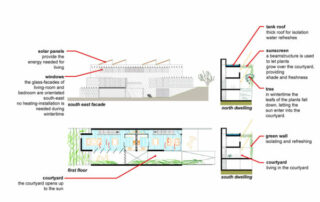
- Housing typology: incorporation of the climatic essence of the patio in the multi-family house.
- Natural ventilation.
- Distribution of the openings inside the houses to favour cross ventilation.
- Design of the openings to control and manage thermal gains or losses, as well as redirect cross ventilation.
- Consumption management. Calculation of energy savings and thermal simulations.
- Introduction of construction elements that favour the environment: cistern cover (green roof that stores rainwater). Pergola (radiation protection in summer).